Introducing fibers and yarns
Fibers can be classified in a variety of ways. It is still one of the most convenient and appropriate classifications of fibers based on whether they are natural or artificial.
Natural fibers are divided into three categories: plant, animal and mineral. A group of natural fibers in the range of polymeric materials obtained from plants and animals. While the other group of natural fibers are obtained from magnesiums. These magnesiums are made of crystalline ceramics. A distinctive feature of natural fibers is that they are generally made from a mixture of different compounds (chemical and physical).
Among the plant fibers, cotton is the most important and most widely used, and the most abundant substance in cotton is cellulose. Other plant fibers include flax, hemp, rye and ramie.
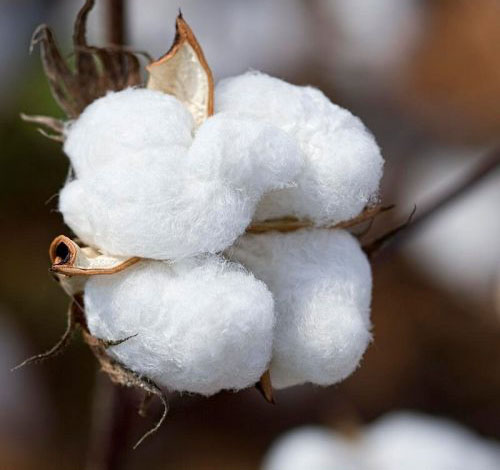

Among animal fibers, the most important and most widely used is wool, the source of which is fleece. Other animal fibers include cashmere, mohair, silk and camel wool.


Mineral fibers include metal fibers, glass, carbon, and asbestos or asbestos.

Synthetic fibers can also be divided into polymer, metal, ceramic or glass fibers. Many developments and advances have taken place in the field of these fibers in the second half of the twentieth century. The use of these fibers as high-performance materials in structural engineering applications is based on three important characteristics:
Small diameter relative to grain size and other microstructural units.
Very high degree of flexibility is one of the characteristics of materials with high modulus and small diameter.
High length to diameter ratio (L / d) which causes a greater proportion of the applied force to be transferred to the fiber-reinforced composite matrix.
Examples of synthetic fibers include cellulose, cellulose acetate, polypropylene, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene, polyamide (nylon), polyester, acrylic and viscous rayon.

The structure and molecular properties of fibers are important factors that have a great effect on the properties of yarn and ultimately fabric, including tensile strength, elasticity, return to elasticity, fiber length and fiber swelling.
By spinning methods and putting the fibers together, yarn is created, which is called narrow and long strands and has various applications in the textile industry.

Yarn in the textile industry is the main component and generally the only component of the fabric. Yarn is also used to connect pieces of fabric.

Yarn classification in terms of material. As mentioned above, this classification includes natural yarn, synthetic yarn and blended yarn, which are produced from natural fibers, synthetic fibers and a combination of the two, respectively.
One of the main characteristics of yarn that makes a difference in the type of application is the grade of yarn. The meaning of yarn grade is its delicacy, which is usually mentioned on the yarn package. Since the yarns are flexible and uneven, instead of measuring the diameter of the yarns, their fineness is expressed in terms of length and weight.
There are two yarn scoring systems: direct system and indirect system.
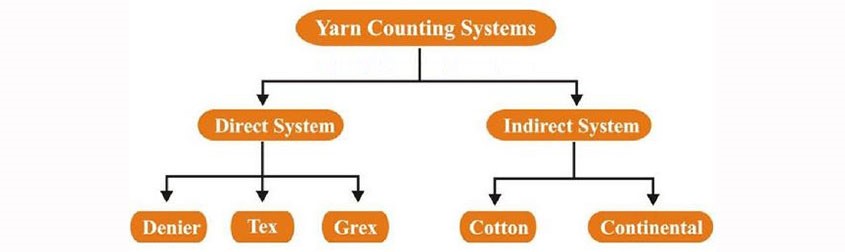
In a straightforward system, a constant length of yarn is considered and its weight is expressed as the yarn score. In this method, fine yarns have a lower score and thicker yarns have a higher score. When buying yarn, depending on the type of work, you should pay attention to its score and prepare a thin or thick yarn suitable for the work. Common units for yarn scores in the direct method are: denier (mass 9000 meters of yarn in grams), tex (mass of 1000 meters of yarn in grams) and metric (length of one gram of yarn in meters).





